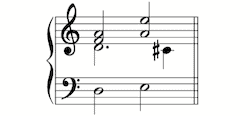What Is a Figura Suspirans?
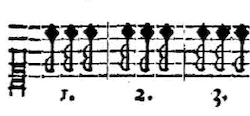
In the second volume of his monumental Phrynis (Mytilenæus) Oder Satyrischer Componist (1677), Wolfgang Caspar Printz (1641–1717) gives the following definition: “Figura Suspirans is nothing other / than a Figura Corta, which instead of the front long note / has a pause half as long and a note equal to the other two.” “Figura suspirans […]
What Is a Figura Suspirans? Read More »